Land Change Modeler is an innovative land planning and decision support system that is fully integrated into the TerrSet software. With an automated, user-friendly workflow, Land Change Modeler simplifies the complexities of change analysis. Land Change Modeler allows you to rapidly analyze land cover change, empirically model relationships to explanatory variables, and simulate future land change scenarios. Land Change Modeler also includes special tools for the assessment of REDD (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation) climate change mitigation strategies. Land Change Modeler provides a start-to-finish solution for your land change analysis needs.
Land Change Modeler Key Features
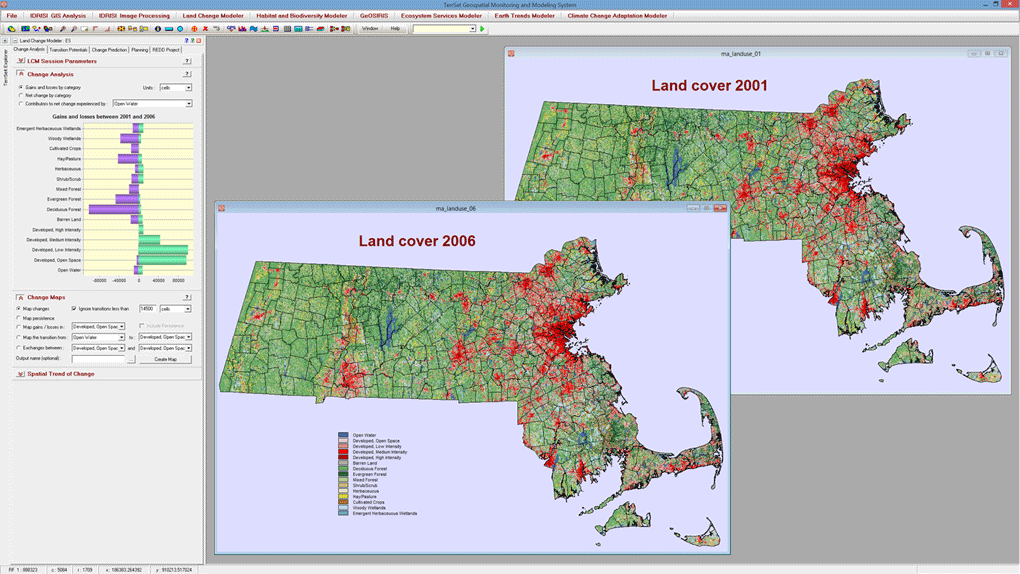
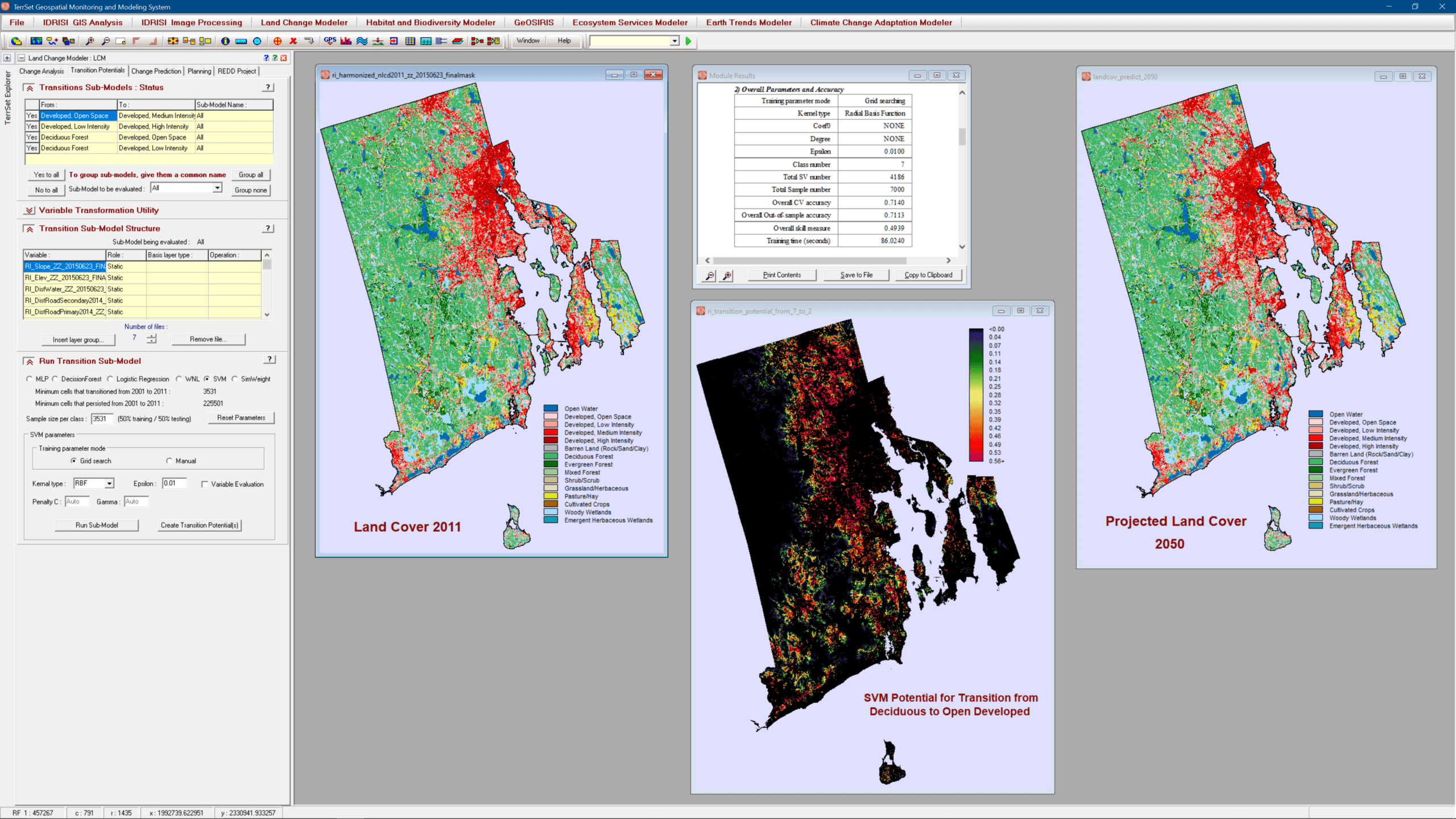
Land Change Analysis
- Quickly generate graphs and maps of land change, including gains and losses, net change, and persistence of specific transitions.
- Uncover underlying trends of complex land change with a change abstraction tool.
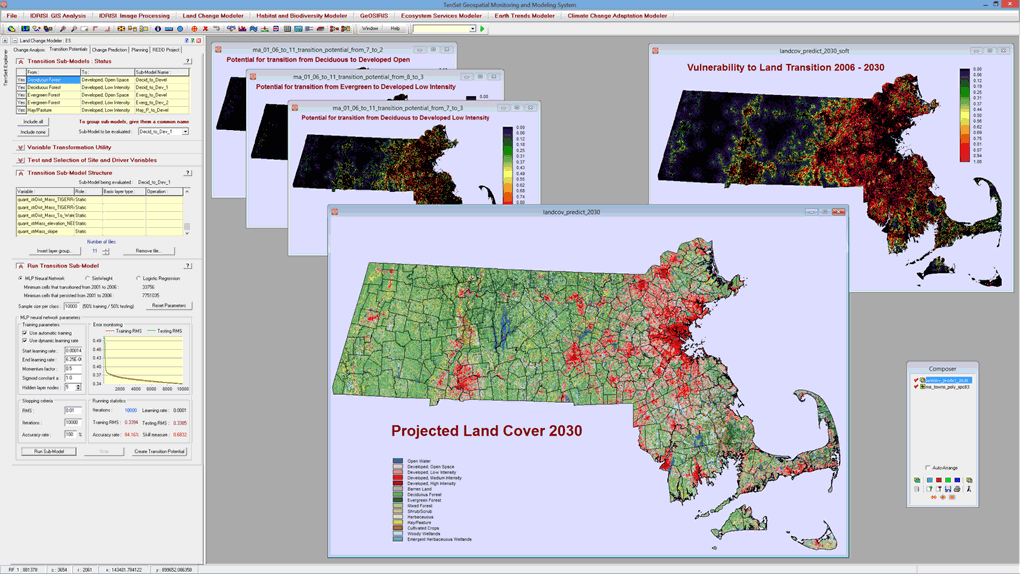
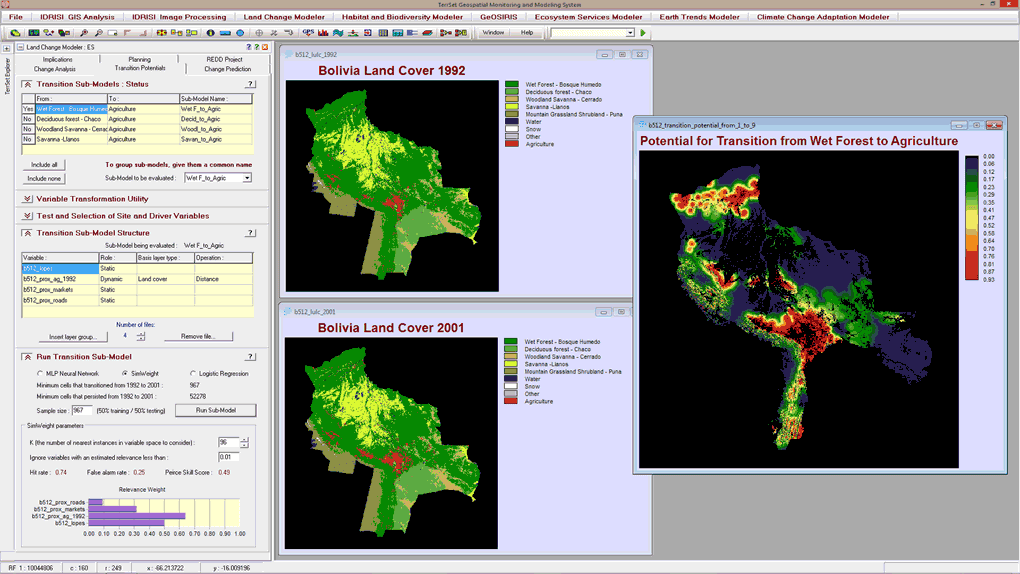
Land Transition Potential Modeling
- Model land cover transition potentials that express the likelihood that land will transition in the future using one of several methodologies-a multi-layer perceptron neural network with full reporting on the explanatory power of driver variables, logistic regression, Decision Forest (Random Forest implementation), Support Vector Machine, Weighted Normalized Likelihood, and SimWeight, a modified machine-learning procedure.
- Incorporate dynamic variables that drive or explain change.
Change Prediction
- Incorporate planning interventions, incentives and constraints, such as reserve areas and infrastructural changes that may alter the course of development when modeling future scenarios.
- Conduct scenario mapping by creating either a hard prediction map based on a multi-objective land competition model with a single realization or a soft prediction map that is a continuous map of vulnerability to change.
- Validate the quality of the predicted land cover map in relation to a map of reality through a 3-way crosstabulation. Hits, misses and false alarms are reported.
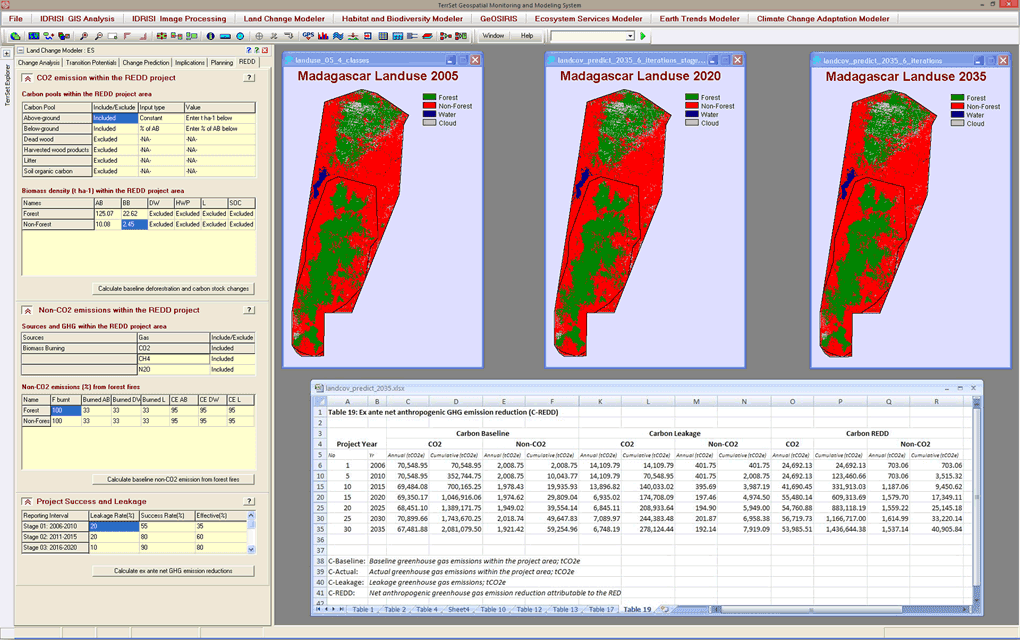
REDD Analysis
- Evaluate REDD related forest conservation strategies and carbon impact scenarios with full GHG emission impact accounting.
- Assess additionality of REDD projects and business-as-usual projection scenarios.
See Bibliography for projects that cite LCM.